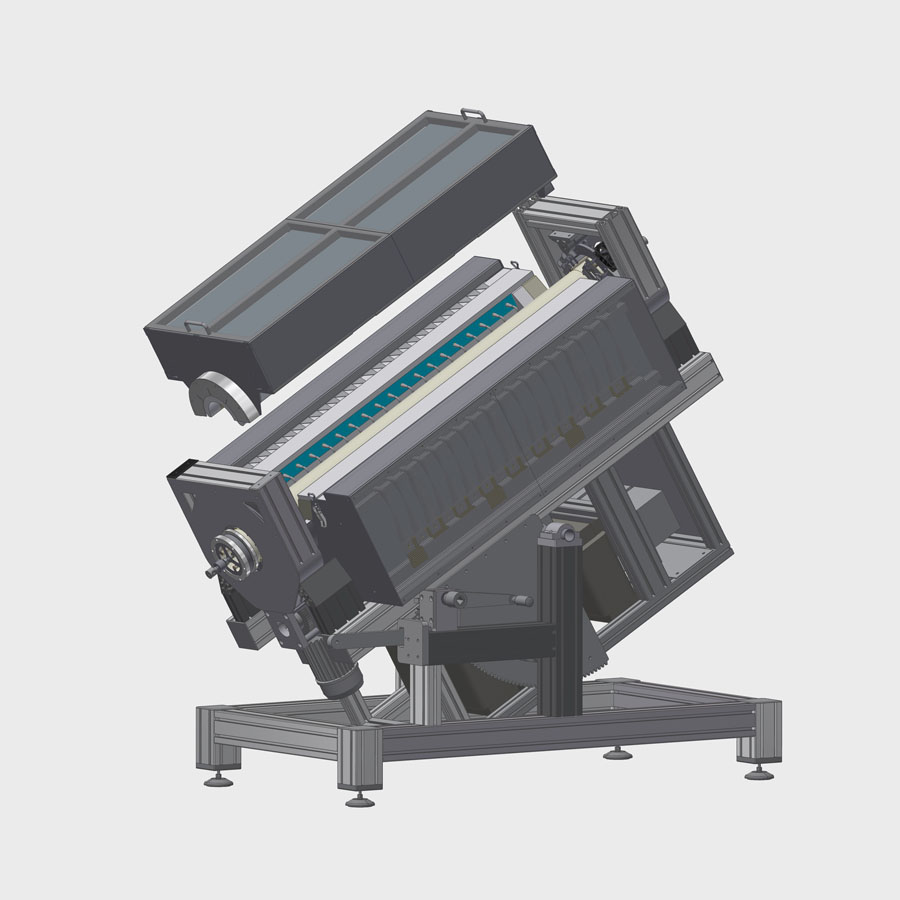
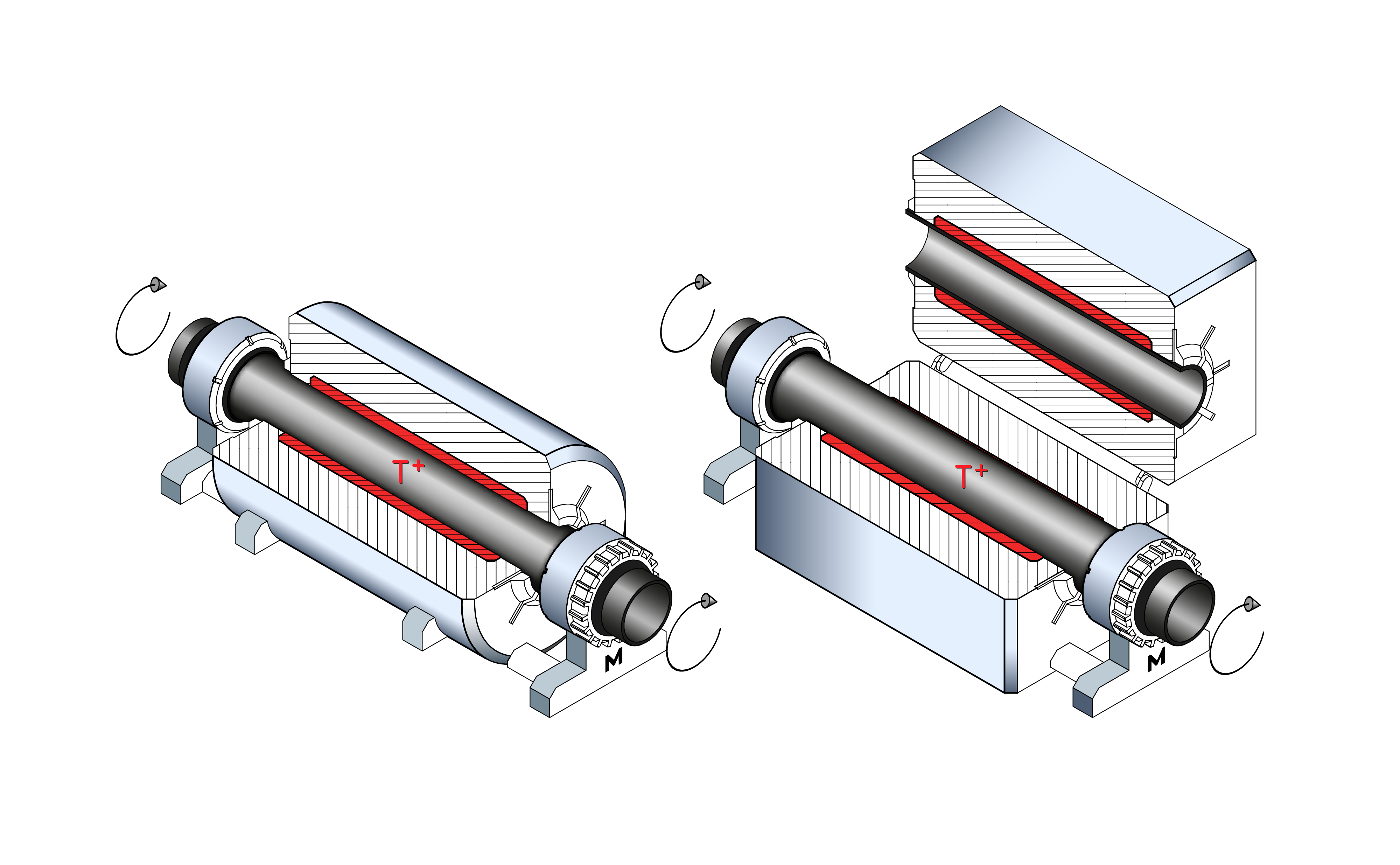
Rotary furnaces
Rotary furnaces are often used for the heat treatment of bulk materials. In them, all materials are uniformly exposed to the heating because their position within the bulk material changes constantly. In addition, a continuous material transport through the heated space can be achieved by slightly and adjustably tilting the rotary furnace.
Rotary furnace batch operation
Rotary furnaces with batch operation are a low-cost rotary furnace variant that combines a heating unit with a rotating vessel and a gas supply system. The focus is on uniform exposure of all bulk material parts.
1. Heating unit: LK-H
Rotary tube materials:
- Vessel (e.g. ampoule or flask) made of quartz glass, ceramic or metal
Short description:
- Temperatures up to 1150 °C or limited by the rotary tube material
- Atmospheres: inert, oxidizing, reducing and vacuum (depending on material and wall thickness of the heated reactor)
- Diameter of the rotating vessel: up to 350 mm
- Heated length: 300 to 600 mm
- Control unit separated from furnace
- Power range up to 4 kW
- Restrictions: Operation only discontinuous
Heating system:
- Single-zoned
Equipment features:
- Wide range of control units with and without PC interfaces
- Software for program and gas control
- Indoor thermocouple
- Systems for gas supply and mixing
- Systems for safe atmosphere change (reducing to oxidizing)
- Swivel drives
Applications:
- Chemical reaction in special atmospheres
- Calcination
- Pyrolysis
- Granulation
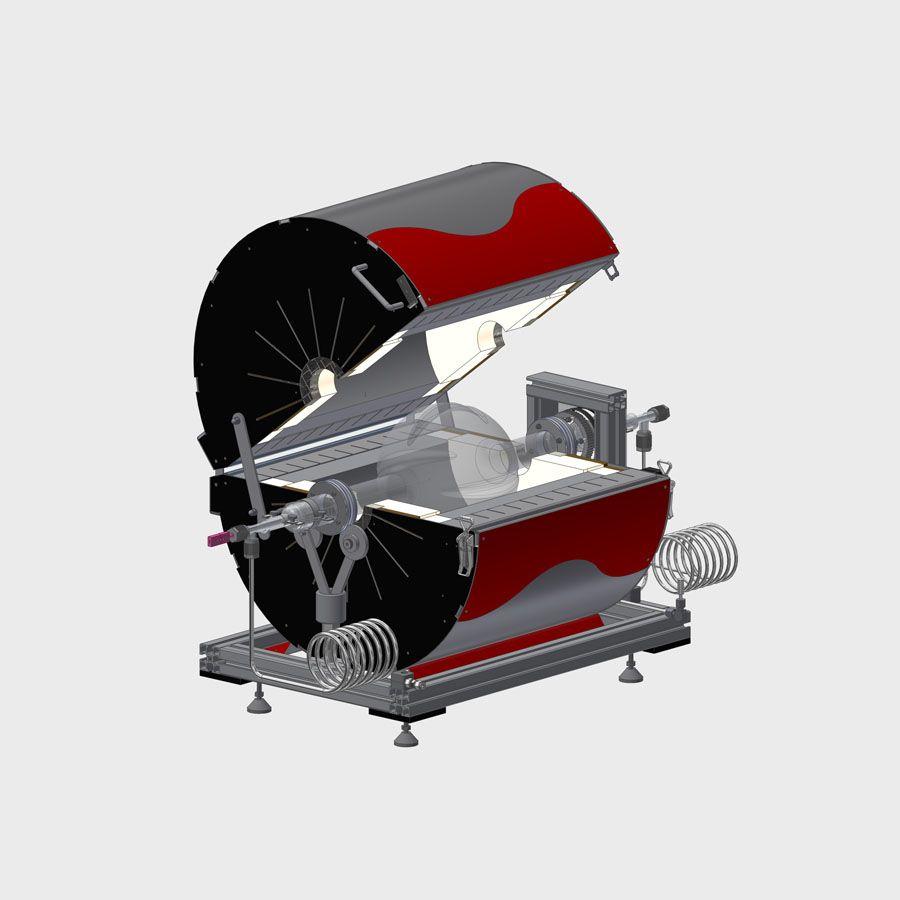
2. Heating unit: LORA-G
Rotary tube materials:
- Vessel (ampoule) made of aluminium oxide
Short description:
- Temperatures up to 1750 °C
- Atmospheres: inert, oxidizing, reducing and vacuum (depending on material and wall thickness of the heated reactor)
- Ampoule diameter: up to 50 mm
- Heated length: 200 mm
- Control unit separated from furnace
- Power range up to 4 kW
- Wall temperature approx. 40 °C
- Restrictions: Operation only discontinuous
Heating system:
- Single-zoned
Equipment features:
- Wide range of control units with and without PC interfaces
- Software for program and gas control
- Indoor thermocouple
- Systems for gas supply and mixing
- Systems for safe atmosphere change (reducing to oxidizing)
- Vacuum pump with measuring device for stand-alone operation
Applications:
- Chemical reaction in special atmospheres at highest temperatures
- Calcination
- Pyrolysis
- Granulation
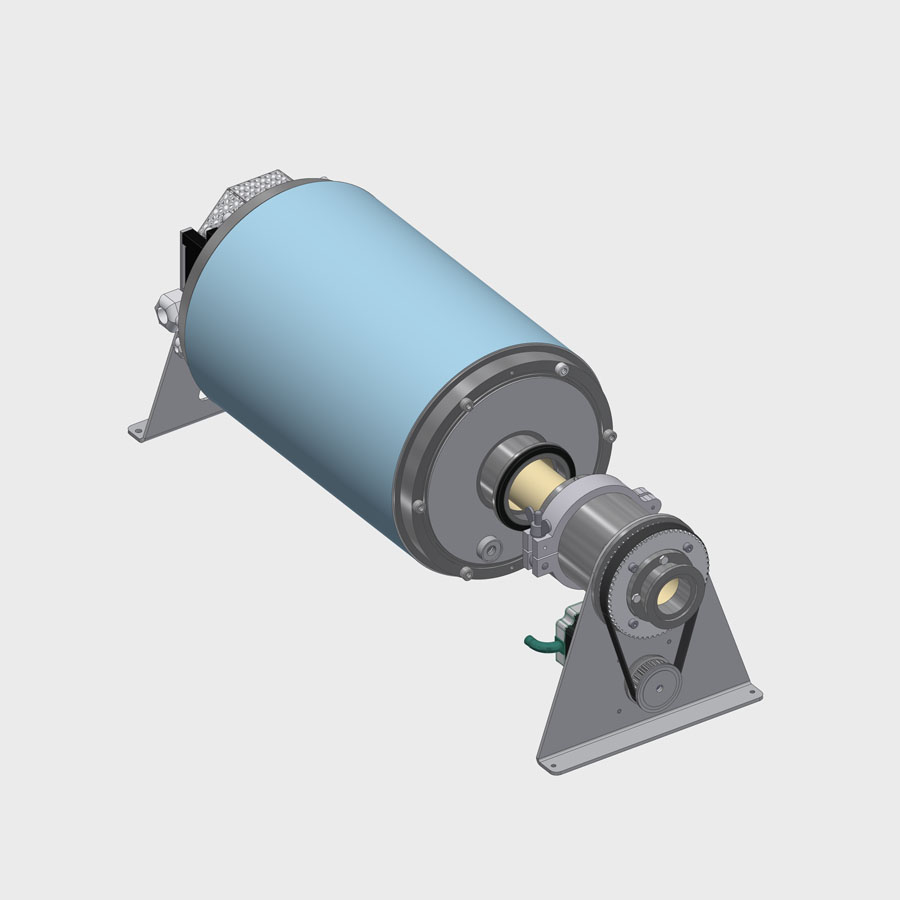
Rotary furnace continuous operation
In addition to the uniform exposure of all bulk material parts, the focus of this rotary furnace is the organization of a continuous material transport through the furnace. Like no other type of furnace, this one requires a special adaptation to the material to be treated. Devices for material input and output as well as for dosing the material flow are function-determining elements and usually have to be adapted to the specific bulk material properties such as pourability, grain size and grain size distribution as well as particle hardness.
Conveyor belts, vibrating troughs, screw conveyors are used for feeding in combination with storage containers, which are often equipped with stirrers and looseners. In many cases, drivers and baffles are used in the rotary furnace to ensure constant material circulation.
The speciality of HTM REETZ is to combine the technical elements of the rotary furnace in such a way that material treatment in defined atmospheres is possible.
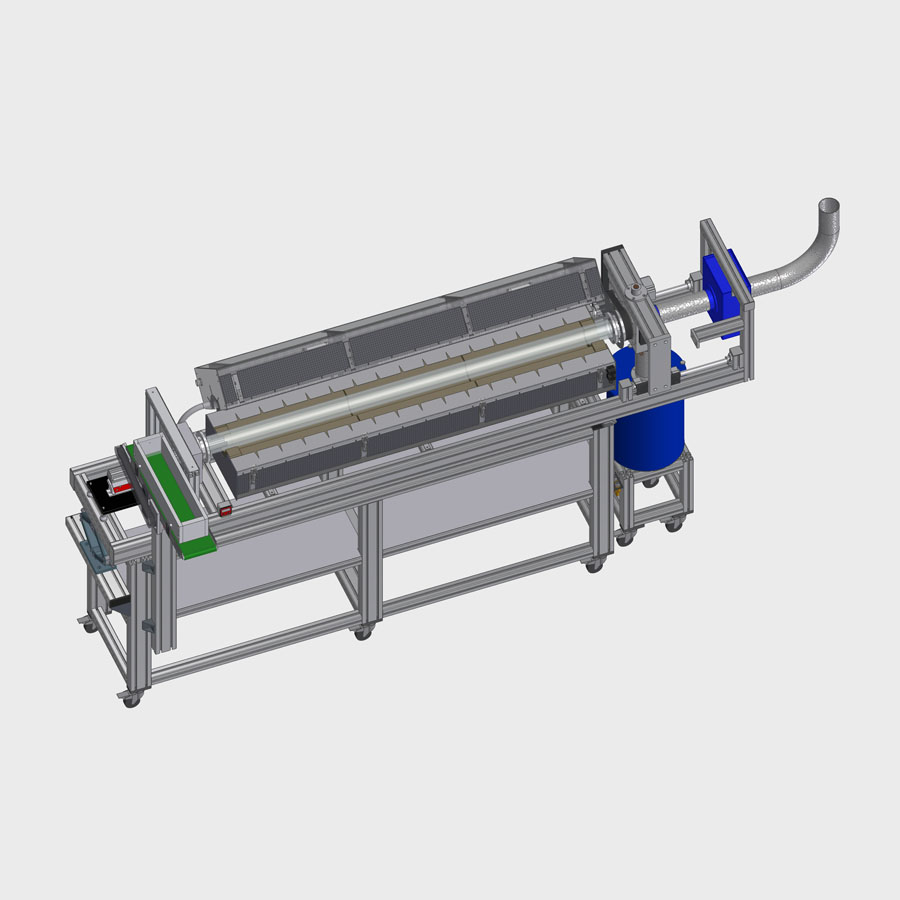
1. Heating unit: LK-H
Rotary tube materials:
- Heat-resistant stainless steels, quartz glass, ceramics
Short description:
- Temperatures up to 1150 °C or limited by the tube material
- Atmospheres: inert, oxidizing, reducing and vacuum (depending on material and wall thickness of the heated reactor)
- Tube diameter: 50 to 250 mm
- Heated length: 250 to 2000 mm*
- Control unit separated from furnace
- Power range up to 36 kW
Heating system:
- Single-zoned
- Multi-zoned
Equipment features:
- Wide range of control units with and without PC interfaces
- Software for controlling rotation, dosing and gas inlets
- Weighing devices for gravimetric dosing
- Systems for gas supply and mixing
- Evaporator for humidifying the atmosphere
- Separator for recovering aerosols from the furnace atmosphere
Applications:
- Chemical reaction in special atmospheres at highest temperatures
- Calcination
- Pyrolysis
- Granulation
* Length determined by available tubes

2. Heating unit: LOSiC
Rotary tube materials:
- Sintered or plasma sprayed ceramic
Short description:
- Temperatures up to 1500 °C or depending on the limit temperatures of the tubes
- Atmospheres: inert, oxidizing, reducing and vacuum (depending on material and wall thickness of the heated reactor)
- Tube diameter: 80 to 250 mm
- Heated length: 250 to 1200 mm*
- Control unit can be installed separately from furnace
- Power range up to 36 kW
Heating system:
- Single-zoned
- Multi-zoned
Equipment features:
- Wide range of control units with and without PC interfaces
- Software for controlling rotation, dosing and gas inlets
- Weighing devices for gravimetric dosing
- Systems for gas supply and mixing
- Evaporator for humidifying the atmosphere
- Separator for recovering aerosols from the furnace atmosphere
Applications:
- Chemical reaction in special atmospheres at highest temperatures
- Calcination
- Pyrolysis
- Granulation
* Length determined by available tubes
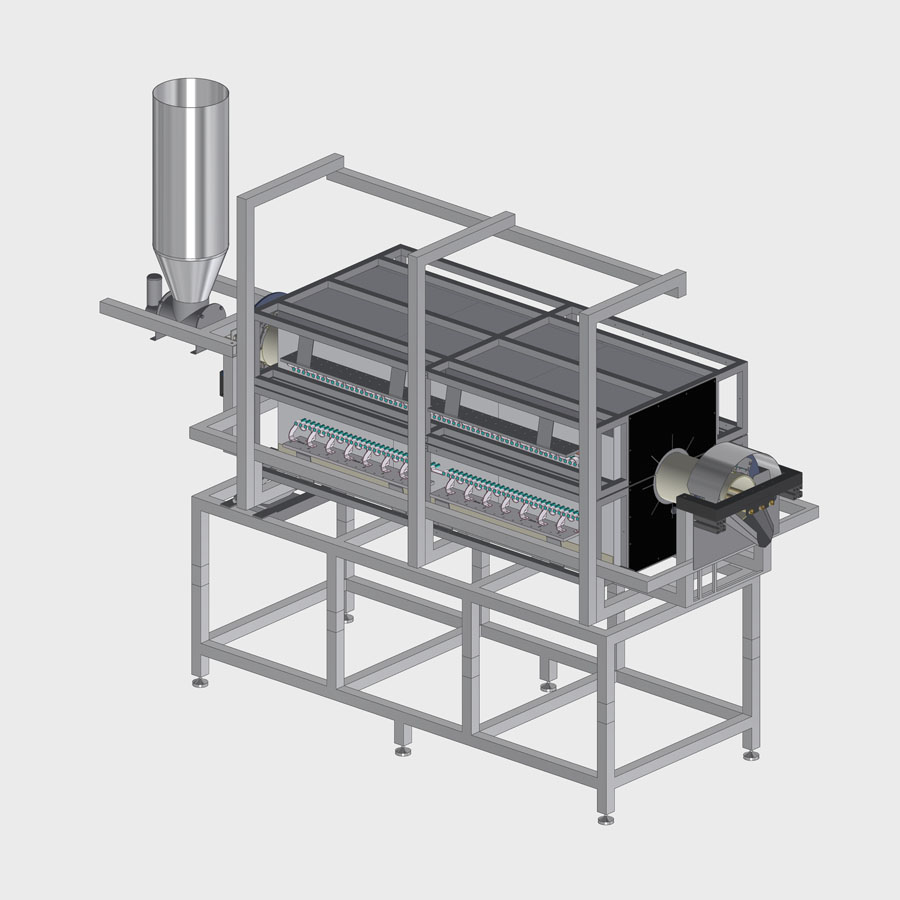
3. Heating unit: LOMOS
Rotary tube materials:
- Sintered or plasma sprayed ceramic
Short description:
- Temperatures up to 1700 °C or depending on the limit temperatures of the tubes
- Atmospheres: inert, oxidizing, reducing and vacuum (depending on material and wall thickness of the heated reactor)
- Tube diameter: 80 to 250 mm
- Heated length: 250 to 1200 mm*
- Control unit separated from furnace
- Power range up to 36 kW
Heating system:
- Single-zoned
- Multi-zoned
Equipment features:
- Wide range of control units with and without PC interfaces
- Software for controlling rotation, dosing and gas inlets
- Weighing devices for gravimetric dosing
- Systems for gas supply and mixing
- Evaporator for humidifying the atmosphere
- Separator for recovering aerosols from the furnace atmosphere
Applications:
- Chemical reaction in special atmospheres at highest temperatures
- Calcination
- Pyrolysis
- Granulation
*Length determined by available tubes